
a) Ultrashort Laser Pulses in the Pico- and Femtosecond Range
Generation and detection of ultrashort light pulses are generally based on nonlinear inter- actions of laser radiation in optical crystals and glasses. They can favorably be used for stret- ching or compressing the pulses or generating new frequencies.Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers
Nonlinear effects and their mutual interaction together with dispersion are of fundamental importance in broadband optical com- munication systems with glass fibers. They can seriously limit the transmis- sion bandwidth and distance between repeaters; on the other hand their ap- propriate and right consideration can significantly improve the operation conditions of a system. The most important nonlinear effects which affect the propagation of pulses in fibers are • Self-Phase Modulation (SPM) • Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) and • Four-Wave-Mixing (FWM) in birefringent fibers Dependent on the peak intensity and shape of the pulses as well as the fiber parameters, in particular the dispersion, these effects are significantly reshaping the pulse form, and there- fore a deeper understanding of these processes is important for an optimum design of a com- munication system.Pulse Compression
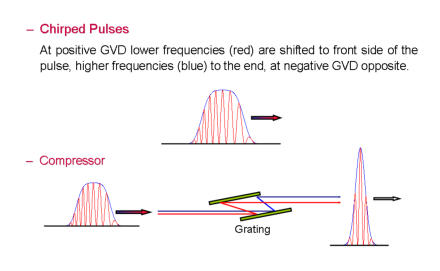
The different nonlinear effects in fibers can also favorably be used via postprocessing to further shorten laser pulses. In a first step these pulses pass a single mode fiber, where they undergo strong SPM with spectral broadening while si- multaneously being stretched due to the fiber dispersion. In a second step these pulses are com- pressed, when they are passing a fre- quency selective delay line in form of an optical grating pair or a prism configura- tion. Under appropriate conditions bandwidth limited pulses reciprocal to their spectral broadening can be generated. In this way pulses from a mode-locked Nd:YAG laser generating pulses of about 70 ps are compressed by a factor of 70 down to 1ps.Additive-Pulse-Modelocking
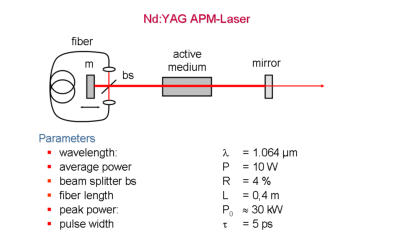
An optical fiber can also be used as part of a conventional laser. In this case spectral broad- ening in the fiber due to SPM counteracts spectral narrowing by the active medium. In a ring configuration pulses from the main laser resonator are launched into both propaga- tion directions of a monomode fiber. When the propagation through the fiber matches the cavity length, self-modelocking is ob- served. For lamp- and semiconductor pumped Nd:YAG-lasers additive-pulse-mode- locking with high average power and pulse widths down to 5 ps can re realized.Fiber-Grating-Raman-Laser
Different to fiber lasers with a doped core like praseodymium-, neodymium- or erbium-fiber lasers the core itself can act as amplifying medium taking advantage of the nonlinear process of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS). Generally this effect allows to generate pulses on new wavelengths (Stokes shift) and with ultrashort pulse widths due to the broad Raman gain pro- file. But the walk-off between Stokes and pump pulses considerably limits the Raman conversion and pulse quality. With a birefringent fiber and taking advan- tage of perpendicular SRS as well as cross phase modulation the group velocity mis- match can be overcome and pulses of 0.8 ps duration at a wavelength of 1.1 µm are gene- rated, which can be tuned over 40 nm in their wavelength by cooling the fiber.Doctoral Theses
M. Kuckartz
Nichtlineare Effekte in optischen Einmoden-Fasern und ihre Anwendungen zur Erzeugung ultrakurzer
Lichtimpulse mit einem Nd:YAG Laser
School of Electrical Engineering, Helmut-Schmidt-Uiversity, Hamburg 1989
R. Schulz Signalausbreitung in Glasfasern unter dem Einfluss nichtlinearer optischer Wechselwirkungen – Erzeugung wellenlängen-abstimmbarer ultrakurzer Lichtimpulse im nahen Infrarotbereich - School of Electrical Engineering, Helmut-Schmidt-Uiversity, Hamburg 1993 H. Groninga Additive Puls Modenkopplung eines Nd:YAG-Lasers – Untersuchungen an einem selbststabilisierenden System - School of Electrical Engineering, Helmut-Schmidt-Uiversity, Hamburg 1999Refereed Publications in Journals and Conference Digests
H. Harde, H. Burggraf Rapid Scanning Autocorrelator for Measurements of Picosecond Laser Pulses Optics Communications 38, 211 (1981) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Combined Action of Stimulated Raman-Scattering and Self-Phase Modulation in Single-Mode Fibers and their Implications on Pulse Compression Technical Digest of Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (Optical Society of America, Washington, D.C., p. 290 (1987) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Theoretical and Experimental Studies of Combined Self-Phase Modulation and Stimulated Raman-Scattering in Single-Mode Fibers Optical and Quantum Electronics 19, 237 (1987) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Operation of a Fiber-Grating Compressor in the Raman Regime Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 1353 (1988) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Stable Compression of Nd:YAG Laser Pulses in the Raman Regime Technical Digest of International Quantum Electronics Conference, Japan Society of Applied Physics, Tokio, p. 154 (1988) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Self-Stabilization of Fiber-Grating Compressor due to Stimulated Raman Scattering Digest of Technical Papers of the European Conference on Quantum Electronics, University Hannover, Hannover, p. ThBA1 (1988) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Subpicosecond Pulse Generation with a Fiber-Grating Raman Laser Digest of Technical Papers of the European Conference on Quantum Electronics, University Hannover, Hannover, p. ThBA2 (1988) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Nonlinear Propagation Effects in Birefringent Fibers Proceedings of the International Congress on Optical Science and Engineering, Nonlinear Materials 1017, Society of Photo-Optics Instruments Engineering, Washington, D.C., p. 234 (1988) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde A Fiber-Grating Raman Laser Generating Subpicosecond Pulses Optics Communications 70, p. 239 (1989) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Tunable Ultrashort Pulse Generation with a Fiber Grating Raman Laser Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, 1989 Technical Digest Series, Vol.11, Optical Society of America, Washington, D.C., p. FA 5 (1989) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Wavelength Tunable Subpicosecond Pulse Generation with a Fiber Grating Raman Laser Applied Physics B 49, p. 263 (1989) R. Schulz, H. Harde A Tunable Ring Laser Based on Perpendicular Raman Scattering International Conference on Quantum Electronics, Technical Digest Series 1990, Vol. 8, Optical Society of America, Washington DC, p. 162 (1990) R. Schulz, H. Harde Four-Wave Mixing and Stimulated Raman Scattering in a Birefringent Fiber International Conference on Quantum Electronics, Technical Digest Series 1992, Vol. 9, Optical Society of America, Washington DC, p. 440 (1992) R. Schulz, H. Harde Pulse Evolution in Birefringent Fibers under the Influence of Four-Wave Mixing and Stimulated Raman Scattering Nonlinear Optics: Materials, Fundamentals and Applications Technical Digest 1992, Optical Society of America, Washington DC, Vol. 18, pp. 395 - 397 (1992) H. Harde, R. Schulz Pulse Generation in Birefringent Fibers by Combined Four-Wave Mixing and Raman Scattering 5th European Quantum Electronics Conference Technical Digest, IEEE Catalog No. 94TH0615-5, ISBN: 0-7803-1791-2, Piscataway, p. 72 (1994) R. Schulz, H. Harde Pulse Generation in Birefringent Optical Fibers by Four-Wave Mixing and Raman Scattering Journal Optical Society America B 12, p. 1279 (1995) H. Groninga, H. Harde Self-Stabilizing Addive Pulse Mode-Locked Nd:YAG Laser Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro Optics Europe 1996, IEEE Catalog No. 96TH8161, ISBN: 0-7803-3169-9, p. 148 (1996) H. Groninga, H. Harde Lamp- and Diode-Pumped APM-Nd:YAG Laser with Self Stabilizing Behavior Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Vol. 11, 1997 OSA Technical Digest Series (Optical Society of America), Washington DC, p. 89 (1997) H. Harde, H. Groninga Coupled-Cavity Mode-Locking - Experimental and Numerical Results of a Self-Stabilizing System Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro Optics Europe 1998, IEEE Catalog No. 98TH8326, ISBN: O-7803-4233, p. 172 (1998) H. Harde Simulation der Pulsausbreitung in Glasfasern Symposium „Simulation in Physik, Informatik und Informationstechnik“, 66. Physikertagung, Leipzig 2002, Herausg. H. Hofman, ISSN 0944-7121, pp. 37-42 (2002)Contributions on National Conferences and Meetings
H. Burggraf, H. Harde Schnell scannender Autokorrelator zur Messung von Pikosekunden Laserimpulsen Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Fachausschuss Kurzzeitphysik, Hamburg, 23. März 1981, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 16, 855 (1981) H. Burggraf, H. Harde Untersuchungen zum Betrieb eines synchron gepumpten modengekoppelten Farbstofflasers mit veränderlicher Pulsrepetitionsrate Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Fachausschuss Kurzzeitphysik, Würzburg, 1. März 1982, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 17, 474 (1982) M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Selbstphasenmodulation in Glasfasern zur Kompression von Nd:YAG Laserimpulsen Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Heidelberg, 17. März 1986, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 21, 722 (1986) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Gemeinsame Wirkung von stimulierter Raman-Streuung und Selbstphasen-Modulation in optischen Glasfasern Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Berlin, 31. März 1987, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 22, Q-7.8 (1987) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Untersuchungen zur Kompression von Nd:YAG Laserimpulsen durch einen Faser-Gitter Kompressor Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Berlin, 31. März 1987, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 22, Q-7.9 (1987) O. Friedrich, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Untersuchungen zum synchronen Pumpen an einem GSGG-Laser Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Berlin, 2. April 1987, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 22, Q-14.8 (1987) M. Kuckartz, R. Schulz, H. Harde Charakterisierung eines Faser-Gitter Kompressors im Raman-Bereich Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Bonn, 23. März 1988, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 23, Q 22 (1988) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Untersuchungen zur Kompression von Stokes-Impulsen durch einen Faser-Gitter Kompressor Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Sektion Quantenoptik, Bonn, 23. März 1988, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 23, Q 21 (1988) R. Schulz, M. Kuckartz, H. Harde Doppelbrechungsabhängige Wellenlängenabstimmung eines Faser-Gitter-Raman Lasers Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Essen, 6. März 1989, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 24, Q 6.3 (1989) R.Schulz, H. Harde Senkrechte Raman-Streuung in doppelbrechenden optischen Fasern Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, München, 13. März 1990, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 25, Q 9.1, 459 (1990) R.Schulz, H. Harde Ein abstimmbarer Faser-Ringlaser unter Ausnutzung von senkrechter Raman-Streuung Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, München, 13. März 1990, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 25, Q 9.2, 459 (1990) R. Schulz, D. Giesecke, H. Harde Untersuchung zur Kompression von Impulsen eines Faser-Raman-Ring-Lasers Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Freiburg, 13. März 1991, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 26, Q 15.2, 841 (1991) R. Schulz, D. Giesecke, H. Harde Ermittlung des Raman-Verstärkungskoeffizienten für senkrechte Raman-Streuung Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Freiburg, 13. März 1991, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 26, Q 15.3, 841 (1991) R. Schulz, H. Harde Vierwellen-Mischung und Raman-Streuung in Optischen Fasern Laserkolloquium Hannover, Hannover, 7. Dezember 1991 R. Schulz, H. Harde Kombinierte Wirkung von Vierwellenmischung und stimulierter Raman-Streuung in doppelbrechenden Fasern Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Hannover, 26. März 1992, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 27, Q 30.7, 1446 (1992) R. Schulz, H. Harde Impulsausbreitung in doppelbrechenden Fasern unter dem Einfluss von Vier-Wellen-Mischung und stimulierter Raman-Streuung Poster Lasertag 1992, Hannover, 2. Dezember 1992 H. Harde, R. Schulz Optisches Wellenbrechen von Stokesimpulsen Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Berlin, 15. März 1993, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 28, Q 11.6, 391 (1993) R. Schulz, H. Harde Nutzung optischer Nichtlinearitäten in doppelbrechenden Fasern zur Erzeugung ultrakurzer Lichtimpulse Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Hamburg, 14. März 1994, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 29, Q 2D.1, 644 (1994) H. Groninga, H. Harde Untersuchungen an einem leistungsstabilisierten APM-Nd:YAG Laser mit frequenzverdoppelndem externen Resonator Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Hamburg, 17. März 1994, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 29, Q 9E.2, 707 (1994) H. Groninga, H. Harde Simulation und Betrieb eines APM-Nd:YAG Lasers Poster Lasertag 1994, Hannover, 7. Dezember 1994 R. Schulz, H. Harde Kombinierte Vier-Wellenmischung und Raman-Streuung in doppelbrechenden Fasern Poster Lasertag 1994, Hannover, 7. Dezember 1994 H. Groninga, H. Harde Vorstellung eines selbststabilisierenden APM-Nd:YAG Lasers Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen u. Österreichischen Physikalischen Gesellschaft, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Innsbruck, 28. Februar 1995, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 30, Q 2D.3, 323 (1995) H. Groninga, H. Harde Der selbststabilisierende APM-Nd:YAG-Laser Poster Lasertag 1995, Hannover, 6. Dezember 1995 H. Groninga, H. Harde Modell für einen selbststabilisierenden APM-Nd:YAG Laser Frühjahrstagung der DPG, Sektion Quantenoptik, Jena, 14. März 1996, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 31, Q 36.6, 284 (1996) H. Groninga, H. Harde Diodengepumpter APM-Nd:YAG-Laser mit hoher Repetitionsrate Poster Lasertag 1996, Hannover, 11. Dezember 1996 H. Groninga, H. Harde Halbleiter gepumpter APM-Nd:YAG Laser mit selbststabilisierendem Verhalten und hoher Repetionsrate Frühjahrstagung der DPG, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Quantenoptik, Mainz, 6. März 1997, Verhandl. DPG (VI) 32, Q 41.3, 351 (1997)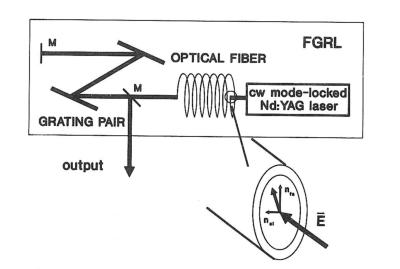

Physics & Climate















